Fintech: General Industry Overview 2017
Industry Overview
Financial Technology (Fintech) companies use computer programs and other technology to support or enable banking and financial services. More broadly Fintech can be defined as any technological innovation in financial services. The financial technology industry is growing significantly and received $17.4 Billion in investment last year alone. The large investment helps illustrate at least institutional investor optimism surrounding the industry. According to EY’s Fintech Adoption Index, nearly a third of worldwide consumers use two or more financial technology services. (Browne, 2017) Companies operating in the Fintech typically exist to provide or improve upon some sort of existing financial infrastructure. Examples include companies such as Robinhood, a mobile-only stock trading app that allows users to trade without any fees, and Lending Club which promises to reduce rates by opening up competition for loans to broad market forces. The total value of the worldwide investment into the fintech industry has grown at about a 48.8% CAGR since 2008, or from approximately $1B to about $24B. The allocation of this funding, at least in the United States has primarily been allocated to peer-to-peer or online lending platforms. (Deloitte, 2017)
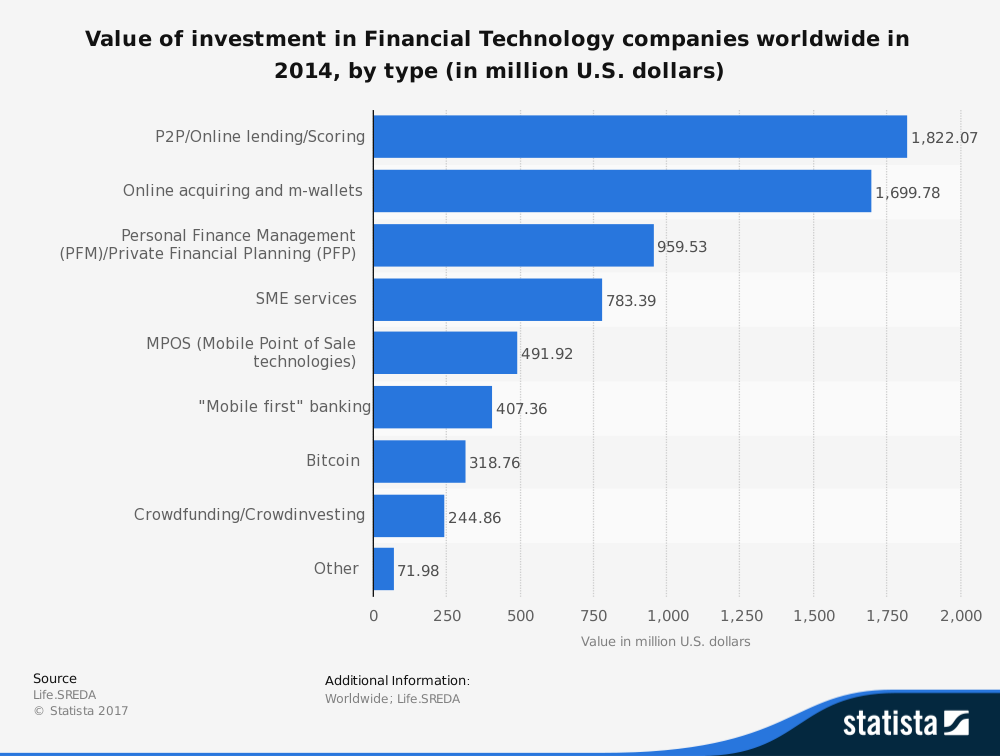
Industry Trends
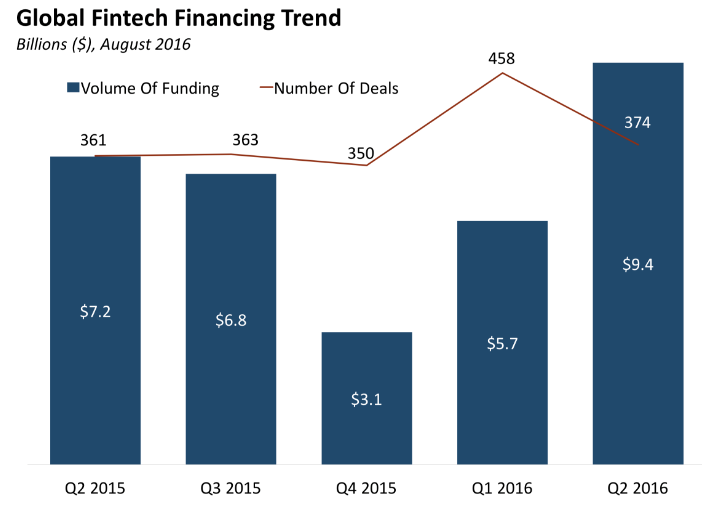
Data for Q2 2015-Q2 2016 shows a significant trend in venture investment into the industry. In fact, total investment into the fintech industry is expected to reach approximately $46B by 2020 according to projections from Deloitte. This implies a projected CAGR of 17.7%. This shows the substantial optimism felt by investors in this space. This optimism stems, in part, from the increased popularity amongst consumers with many of the technologies being created by financial technology companies.
The blockchain and cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin and ether are receiving considerable attention in the industry right now. Blockchain is a form of distributed ledger technology (DLT). This means that it maintains records of all cryptocurrency transactions on a distributed network of computers, but has no central ledger. (Browne, 2017) The idea of blockchain is that it should provide transparency for a multitude of different industries. While blockchain was initially explored by the Financial Services sector, the potential of this technology is now being realized by all sectors, including energy, telecoms, and pharma. The technology is moving from hype to reality and we will likely see business use cases becoming more common.
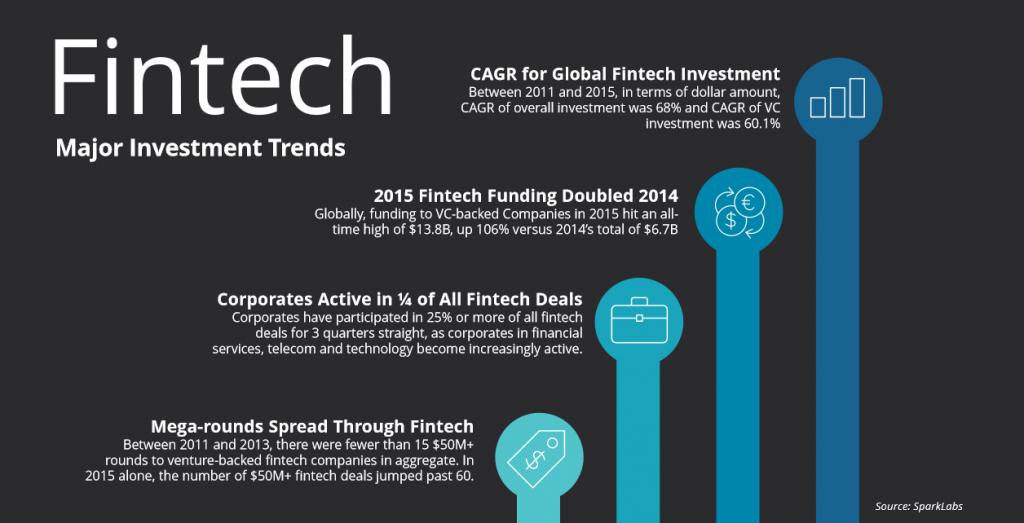
Majors Players in the Industry
The financial technologies industry is extremely saturated with no dominating players and is becoming more and more saturated with the increased number of fintech companies entering the market; however, there are a few major players worth mentioning.
LendingClub Corporation, together with its subsidiaries, operates as an online marketplace that connects borrowers and investors in the United States. Its marketplace facilitates various types of loan products for consumers and small businesses, including unsecured personal loans, unsecured education and patient finance loans, auto refinance loans, and small business loans and lines of credit. The company also offers investors an opportunity to invest in a range of loans based on term and credit characteristics.
PayPal Holdings, Inc. operates as a technology platform company that enables digital and mobile payments on behalf of consumers and merchants worldwide. It enables businesses of various sizes to accept payments from merchant Websites, mobile devices, and applications, as well as at offline retail locations through a range of payment solutions, including PayPal, PayPal Credit, Braintree, Venmo, Xoom, and Paydiant products. The company’s platform allows consumers to shop by sending payments, withdraw funds to their bank accounts, and hold balances in their PayPal accounts in various currencies.
Kabbage Inc. provides online business loans to small businesses and funding companies. It operates a financial services data and technology platform to provide fully automated funding to businesses. The company was founded in 2009 and is based in Atlanta, Georgia.
Stripe, Inc. develops APIs and tools that enable businesses to accept and manage online payments. The company supports international debit or credit cards, including Visa, MasterCard, American Express, Discover, Diners Club, and JCB. It serves Web and mobile businesses in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, Australia, and various European countries. Stripe, Inc. was formerly known as DevPayments.
Robinhood Financial, LLC provides stock trading services to buy and sell stocks. It offers stock brokerage services to invest in publicly-traded companies and exchange-traded funds listed on U.S. exchanges. The company was founded in 2013 and is headquartered in Palo Alto, California.
Previous & Recent Transactions
The acquisition of Fintech companies is becoming more common as many companies in the industry are realizing that they need to acquire growth to have a shot at maintaining their position in the industry. PayPal has been extremely active in acquiring companies in the space as it seeks to maintain control over the online payments system, this strategy is evident in their acquisition of Braintree in 2013 for $800m. This acquisition gave them control of Braintree as well as Venmo allowing PayPal to have an even tighter grip of the total online payments transactions. This seems to be a universal strategy within the financial technologies industry.
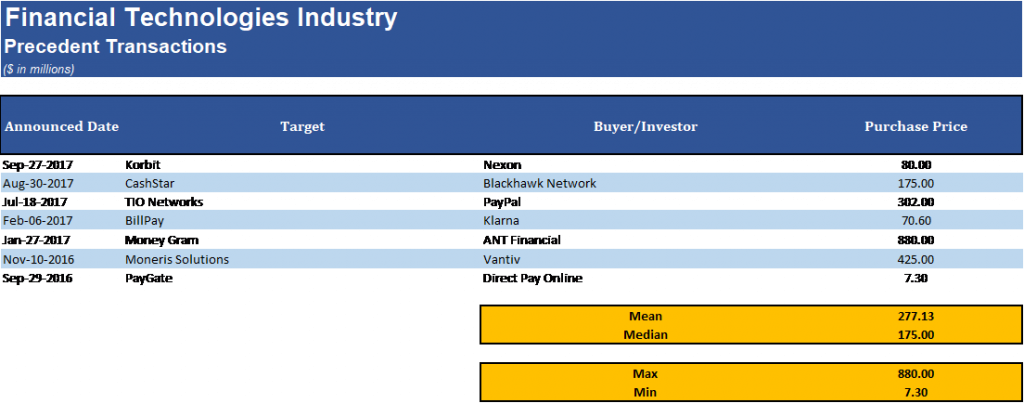
Opportunities
Enormous Market Size: The most significant opportunity presents itself in fintech’s ability to disrupt the financial services industry. The financial services industry is approximately $25 trillion annually and companies within the financial technology sector that are able to disrupt this often inefficient industry, they will be able to gain massively from this disruption.
Willing and Able Acquirers: The major participants in financial services are actively seeking new technology solutions to remain relevant and gain competitive advantages. Their willingness to adopt new technology provides tailwinds to startups looking to engage the industry. The number of new fintech businesses being created is at an all-time high.
Customer Access: The access to the technologies (mobile, cloud, networks, analytics) necessary to enable financial technology is at an all-time high and allows easy access to consumers. This ease of access is one of the major drivers of the many new start-ups being created, many entrepreneurs see the market and way to access it as too good of an opportunity to pass up on.
Risks
Regulation: The most significant risk is regulation surrounding fintech. Financial services is heavily regulated and fintech is getting more attention from policy makers. Governments at all levels have taken an increasing interest in the financial services industry, post the global financial crisis. Old and new policies will have a significant effect on the success and failure of new companies.
Although there are strong sentiments in the market currently that believe the current administration will cut back on much of the regulation that has been placed upon the financial services industry, there is no guarantee of this. An increase in regulation on fintech could have a significant impact on the industry.
Participant Hesitancy: Although many banks are actively seeking newer and improved technologies to replace the often dated current technology, there are often massive complications in this transition. These complications can dissuade industry participants and is an important risk that needs to be considered.
References
20 Game Changing Consumer Tech M&A Deals, CB Insights Research (2017), https://www.cbinsights.com/research/consumer-tech-acquisition-merger-deals/ (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
Fintech investment areas worldwide (2017) 2014 | Statistic Statista, https://www.statista.com/statistics/376891/value-of-global-fintech-investment-areas/ (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
Follow FinTech on Index.co, Index.co, https://index.co/market/fintech/acquisitions (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
In 2017, Challenges and Opportunities in Fintech, https://www.tsys.com/news-innovation/whats-new/Articles-and-Blogs/nGenuity-Journal/in-2017-challenges-and-opportunities-in-fintech.html (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
Investopedia, Fintech Investopedia (2017), https://www.investopedia.com/terms/f/fintech.asp (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
Lauren Gensler, The 10 Biggest Fintech Companies In America Forbes (2017), https://www.forbes.com/sites/laurengensler/2017/08/08/biggest-us-fintech-companies/#1ac3b8dd59d8 (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
Ryan Browne, EVERYTHING YOU’VE ALWAYS WANTED TO KNOW ABOUT FINTECH CNBC (2017), https://www.cnbc.com/2017/10/02/fintech-everything-youve-always-wanted-to-know-about-financial-technology.html (last visited Nov 16, 2017)
Value of Fintech investments globally (2017), 2020 | Statistic Statista, https://www.statista.com/statistics/502378/value-of-fintech-investments-globally/ (last visited Nov 16, 2017).
Justin Ricks contributed to this article.
- Covid-19 Impact on US Private Capital Raising Activity in 2020 - May 27, 2021
- Healthcare 2021: Trends, M&A & Valuations - May 19, 2021
- 2021 Outlook on Media & Telecom M&A Transactions - May 12, 2021
